Sometimes I think about how this universe came into being, what’s the story behind it, and you know what I find out? The story of the universe is also a story of an atom. From where did it all originate? Atoms are the first step in the solution; they were created in the early universe, formed in stars, and dispersed throughout space. These days, they mold every substance, living creature, and even the water drop.
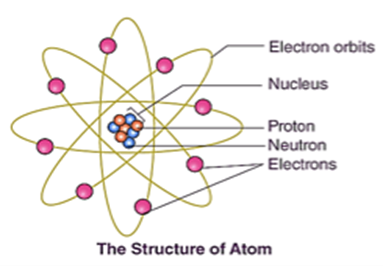
Let’s talk about what an atom actually is, the smallest unit of matter that nevertheless possesses all of an element’s chemical characteristics is an atom. Solids, gases, and liquids are created by the interaction of molecules, which are made up of atoms. For instance, water molecules are made up of atoms of oxygen and hydrogen that have joined together.
Protons, electrons, and neutrons are the three fundamental particles that make up an atom. The positively charged protons and the neutral neutrons are found in the atom’s nucleus, or center. The electrons (negatively charged) are found in the outermost parts of the atom, which are referred to as electron shells. The quantity and configuration of an atom’s fundamental particles determine its characteristics.
The image of atomic structure was completed with the discovery of the neutron. Similar to protons, neutrons exist in an atom’s nucleus but are chargeless. An atom’s place in the periodic table of elements is determined by its atomic number, which is based on the number of protons in its nucleus. Different isotopes of an element can result from variations in the number of neutrons in an atom’s nucleus. Isotopes differ in their neutron counts but share the same number of protons.
Around the nucleus, an atom’s electrons occupy shells, or energy levels. The farther you are from the nucleus, the more energy these shells have. The valence shell, which is the outermost shell, contains the electrons that give an element its chemical characteristics. An element’s reactivity and capacity to form chemical bonds are determined by the number of electrons in its valence shell.
Here comes the interesting part of atomic structure, i.e., types of atomic bond, which show us why atomic structure is important. It includes basically three types, which are ionic, covalent, and metallic bonding. Ionic bonds are created when atoms with significantly different electronegativity donate electrons to one another, creating ions with opposing charges, which form rigid but fragile structures. While sharing one or two pairs of electrons for stabilizing the electronic configuration creates a covalent bond, as seen in diamond. On the other hand, delocalized electrons that are free to travel across the substance form metallic bonds between metal atoms. Metals’ high electrical conductivity and malleability are caused by metallic bonding.
Since it serves as a basis for comprehending chemical reactions, elemental characteristics, and matter behavior, an understanding of atomic structure is essential to all facets of chemistry. Applications of atomic structure are useful in a variety of domains, such as materials research, nanotechnology, and medicine.
https://byjus.com/jee/atomic-structure/
https://www.numberanalytics.com/blog/atomic-structure-essentials-materials-science
![]()