The smallest repeating atomic structure in a crystal is known to be the unit cell. The structure of a crystal is made up of repetitions of these unit cells. You can determine the entire crystal structure if you know the unit cell arrangement.
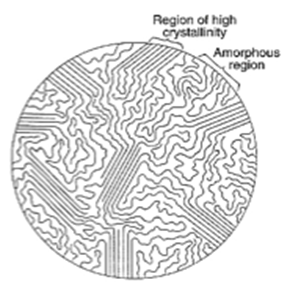
The degree of long-range order in a material’s crystal structure is described by its crystallinity, which shows how closely the material resembles the ideal repeat of the crystal-building pattern. It simply refers to a solid’s level of structural organization. The arrangement of atoms or molecules in a crystal is periodic and regular. An intermediate situation is represented by amorphous materials, which have a disordered structure having random arrangements. Examples of these materials include liquids and glasses.
Several parameters, such as the geometry of the repeat unit, the molecular weight, and the temperature history, determine whether a polymer is crystalline or amorphous. The lengthy chains of polymers make their crystallinity more difficult than that of other materials. Semi-crystalline polymers sometimes contain crystalline patches scattered throughout amorphous material because the polymer chains may align and pack collectively to form crystals in some places while being disordered in others.
Amorphous materials are softer and weaker than crystalline ones because of their structure, whereas ceramics and metals have higher mechanical strength due to their higher crystallinity. Low crystallinity materials, such as PE (polyethene), have a high degree of flexibility.
Crystalline materials possess high melting temperatures, which means it takes greater force to shatter them than amorphous ones, and a tendency to reflect light due to their packed structure. Because of the crystalline material’s dense structure, it is chemically resistant, meaning that no chemical can readily dissolve it.
High-density polyethene (HDPE) is made up of linear chains that don’t branch much. The close packing of molecules results in a high degree of order. It is utilized for drainpipes and milk bottles since it is dense and hard as a result. On the other hand, low-density polyethene (LDPE) has a lot of short branches that make it difficult for molecules to pack closely together and create an orderly structure. It can be used in films like plastic carrying bags and food wrapping because of its decreased density and stiffness.
https://firstyearengineer.com/material-science/introduction/crystal-structure/
https://www.victrex.com/en/blog/2017/polymer-crystallinity-hpp-explained-part-3
![]()